Academic Writing
|
What to write as an BA student?
Top |
How to complete an BA assignment?
1. General construction of a paper
Introduction:

( # elective item)
The content of an introduction is normally in the following sequence: the purpose and the nature of the current research, the research questions and the research value.
Body( in different structures)
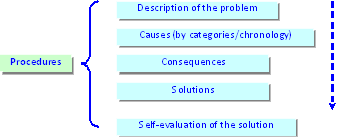
- Chronology
- Comparison and contrast
- Pros and cons
- Research methods/ findings/ discussion
Conclusion
Conclude the findings. Do not add anything that is not discussed.
(Evans, 2010)
2. Tips on good writing
Procedures:
- Understanding the audience
- Formulating a temporary argument in essay writing
- Reading around the subject
- Following the writing objective
- Outlining your paper
- Having plenty of time to write
- Revising at least twice
(Silber, 2011)
Language features
- Use more technical or academic words:
Academic word list from Victoria University of Wellington
Academic words check from Web VP 1.5
The more efficient a sentence is the more content words it contains.
- Adopt hedging techniques:
- Hedging expressions: seem, appear, suggest, indicate estimate, assume, according to, on the basis of, on the evidence of…
- Modal verbs: may, might, could, can…
- Adverbs: probably, possibly, perhaps, seemingly…
- Nouns: probability, possibility, assumption, evidence…
- Generalization:
tend/ have a tendency to; generally, largely, primarily, for the most part; apart from, except for…
(Evans, 2010)
Other tips on writing:
- Making a rough plan and following it
- Writing up sessions orderly
- Completing the paper in the order comfortable to you (The method is often a good start.)
- Finding a quiet place to write and stay at the same place
¡]Philips & Pugh, 1996)
Top
|
What to read about the subject?
1. Books:
- Make use of resources in
 and and 
- Find specific books on
 . .
2. Journals:
- Photocopy articles from hardcopy journals on 5th floor in the library.
- Search e-resources with PolyU library databases:
3. Internet resources
 provides abundant sources but its reliability may be low. provides abundant sources but its reliability may be low. - Scholars' personal website
Top
|
How to read critically?
1. Understand the framework
- Abstract
- Body: Introduction
 Methods/ Materials Methods/ Materials Results Results Discussion Discussion
- Conclusion
2. Get the most of what you read quickly
- Books: Preface
 Tables Tables Contents and index Contents and index other content around your topic other content around your topic
- Journals: Abstract
 Thesis statement (statement of your position) and conclusion Thesis statement (statement of your position) and conclusion
3. Critical Reading — Read looking for the way of thinking
- Understanding the text
- Evaluating it with your knowledge
- Considering the way to use the portion of the text in the argument of your writing
4. Note-taking:
- Taking notes on separate cards or files
- Categorizing them after reading
- Recording your pop-up thoughts
- Putting relative bibliographic information of your source in a computer file
(Knott, 2011)
Top
|
How to compile a literature review?
1. Introduction
- Defining the topic and objectives of the review
- Conveying to your audience SOME previous studies on a subject
- Classifying different studies in the area
- Indicating the gap of the previous studies
2. Preparation
Read and notice:
- the main issues or problems under discussion;
- general attitudes towards the issue across the collected literature;
- writers' ground for disagreement (difference in research questions, theories or approach); and
- any changes of issues chronologically. Keep notes on the links between articles while reading.
(Taylor, 2011)
3. Writing strategies
Generic structure of a literature review:
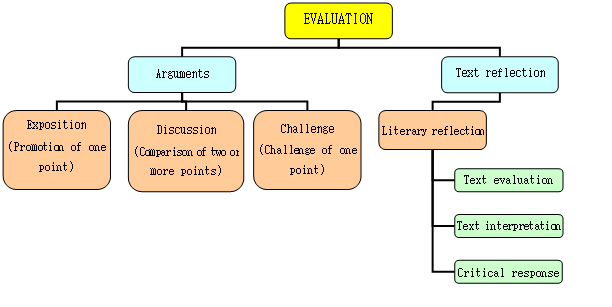
(Simpson, 2011)
Structure of a literature review
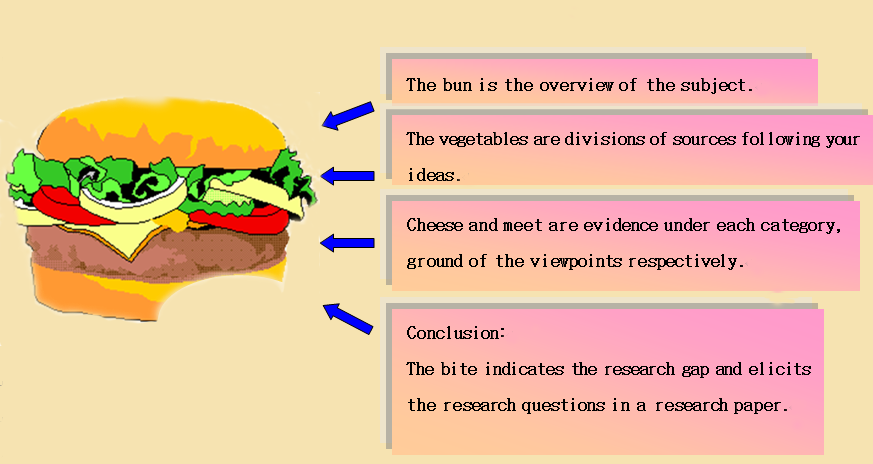
Integrate views from sources:
state, maintain, remark, propose, observe, suggest, declare, define, emphasize, comment, report, assert…
…’s study shows that, from…’s results, it may follow that…
- Use a variety of connectives:
furthermore, therefore, consequently, hence, in other words, that is…, thus, in contrast, unlike…, whereas, on the contrary, as a matter of fact, in fact...,
(Criollo, 2003)
4. Literature review samples
Top |
Other online resources
1. Writing devices
2. Literature review
3. Research proposal writing
4. Editing and proofreading.
Top
|
 |
|




